combinational and sequential logic circuits
In any digital device,
like a computer or a tablet. You will find a number of digital circuits.
Digital circuits are essentially circuits that operate on the digital concept
of 0s and 1s. Which means they switch on or off. So we can say that they have a
unique job of switching on the application of a certain logic. And what do we
mean by logic? Essentially a specific arrangement of binary codes.
Consequently, these digital circuits are also known as switching circuits.
There are two main types of digital logic circuits in digital electronics.
Combinational and sequential logic circuits.
What are combinational logic circuits?
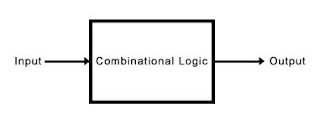
Combinational circuits
are a basic collection of logic gates. Their outputs depend only on the current
inputs. Combinational circuits are also time independent. Along with the
absence of concepts like past inputs, combinational circuits also do not
require any clocks. The result of these properties is a simple circuit capable
of implementing complex logic using only logic gates. An easy to understand
example is a full adder.
Block diagram of a combinational logic circuit
What are the different types of combinational
logic circuits?
1.
Arithmetic and logical
combinational circuits – Adders, Subtractors, Multipliers, Comparators.
2.
Data handling
combinational circuits – Multiplexers, Demultiplexers, encoders, decoders.
3.
Code converting
combinational circuits – Binary to Gray,
Gray to Binary, seven segment etc.
What are sequential logic circuits?
Sequential
circuits are a collection of memory elements. These memory elements are
flip-flops.
These circuits are capable of “remembering” data. Hence, a sequential circuit’s output depends on current input, as well as past input. Moreover, since flip-flops are present the output of a sequential circuit also depends on the clock input. These circuits are quite complex. They are capable of implementing complex logic with memory. Add a memory element and feedback to a combinational circuit and you get a sequential circuit.
These circuits are capable of “remembering” data. Hence, a sequential circuit’s output depends on current input, as well as past input. Moreover, since flip-flops are present the output of a sequential circuit also depends on the clock input. These circuits are quite complex. They are capable of implementing complex logic with memory. Add a memory element and feedback to a combinational circuit and you get a sequential circuit.
Block diagram of a sequential
logic circuit
What are the different types of
sequential logic circuits?
1.
Synchronous circuits- The same clock input synchronizes all the
memory elements. As in synchronous counters.
2.
Asynchronous circuits- An external clock is absent. However, the
clock inputs receive pulse inputs from other sources/elements in the circuit.
Example: Asynchronous counters.
What are the differences
between combinational and sequential logic circuits?
These have memory and are used
to design memory storage devices
Combinational Logic
Circuits
|
Sequential Logic
Circuits
|
Output depends only on current inputs
|
Output depends on current, past as well as clock inputs
|
Hence they are faster
|
They are slower
|
They are time-independent and don’t need clock inputs
|
Time-dependent and thus require clocks
|
Since there is no clock they don’t require triggering
|
Since a clock is present, triggering is required
|
Made using logic gates
|
Made using flip-flops
|
Also, easier to design since there are no crazy feedbacks
or clocks
|
More complicated to design
|
They can’t store anything. They have no memory.
|
|
Main uses are to implement arithmetic and logical
operations.
|
Main use is for storing data and other memory applications
|
Easier to use and handle
|
Harder to use and handle
|
Example: Full Adder, Multiplier etc.
|
Example: Counters, Shift-registers
|



Comments
Post a Comment