microprocessor
A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer, fabricated on a small chip capable of performing ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit) operations and communicating with the other devices connected to it.
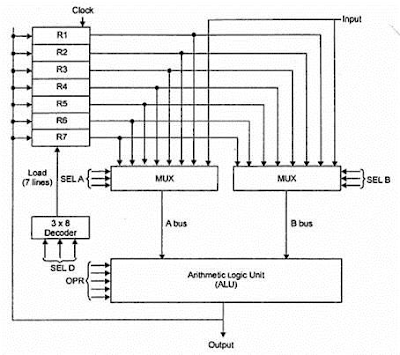
Microprocessor consists of an ALU, register array, and a control unit. ALU performs arithmetical and logical operations on the data received from the memory or an input device. Register array consists of registers identified by letters like B, C, D, E, H, L and accumulator. The control unit controls the flow of data and instructions within the computer.
Block Diagram of a Basic Microcomputer

How does a Microprocessor Work?
The microprocessor follows a sequence: Fetch, Decode, and then Execute.
Initially, the instructions are stored in the memory in a sequential order. The microprocessor fetches those instructions from the memory, then decodes it and executes those instructions till STOP instruction is reached. Later, it sends the result in binary to the output port. Between these processes, the register stores the temporarily data and ALU performs the computing functions.
List of Terms Used in a Microprocessor
Here is a list of some of the frequently used terms in a microprocessor −
- Instruction Set − It is the set of instructions that the microprocessor can understand.
- Bandwidth − It is the number of bits processed in a single instruction.
- Clock Speed − It determines the number of operations per second the processor can perform. It is expressed in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz).It is also known as Clock Rate.
- Word Length − It depends upon the width of internal data bus, registers, ALU, etc. An 8-bit microprocessor can process 8-bit data at a time. The word length ranges from 4 bits to 64 bits depending upon the type of the microcomputer.
- Data Types − The microprocessor has multiple data type formats like binary, BCD, ASCII, signed and unsigned numbers.
Features of a Microprocessor
Here is a list of some of the most prominent features of any microprocessor −
- Cost-effective − The microprocessor chips are available at low prices and results its low cost.
- Size − The microprocessor is of small size chip, hence is portable.
- Low Power Consumption − Microprocessors are manufactured by using metaloxide semiconductor technology, which has low power consumption.
- Versatility − The microprocessors are versatile as we can use the same chip in a number of applications by configuring the software program.
- Reliability − The failure rate of an IC in microprocessors is very low, hence it is reliable.
- Multiprocessor means a multiple set of processors that executes instructions simultaneously. There are three basic multiprocessor configurations.
- Coprocessor configuration
- Closely coupled configuration
- Loosely coupled configuration
Coprocessor Configuration
A Coprocessor is a specially designed circuit on microprocessor chip which can perform the same task very quickly, which the microprocessor performs. It reduces the work load of the main processor. The coprocessor shares the same memory, IO system, bus, control logic and clock generator. The coprocessor handles specialized tasks like mathematical calculations, graphical display on screen, etc.The 8086 and 8088 can perform most of the operations but their instruction set is not able to perform complex mathematical operations, so in these cases the microprocessor requires the math coprocessor like Intel 8087 math coprocessor, which can easily perform these operations very quickly.Block Diagram of Coprocessor Configuration

Closely Coupled Configuration
Closely coupled configuration is similar to the coprocessor configuration, i.e. both share the same memory, I/O system bus, control logic, and control generator with the host processor. However, the coprocessor and the host processor fetches and executes their own instructions. The system bus is controlled by the coprocessor and the host processor independently.Block Diagram of Closely Coupled Configuration

How is the processor and the independent processor connected?
- Communication between the host and the independent processor is done through memory space.
- None of the instructions are used for communication, like WAIT, ESC, etc.
- The host processor manages the memory and wakes up the independent processor by sending commands to one of its ports.
- Then the independent processor accesses the memory to execute the task.
- After completion of the task, it sends an acknowledgement to the host processor by using the status signal or an interrupt request.
Loosely Coupled Configuration
Loosely coupled configuration consists of the number of modules of the microprocessor based systems, which are connected through a common system bus. Each module consists of their own clock generator, memory, I/O devices and are connected through a local bus.Block Diagram of Loosely Coupled Configuration

Advantages
- Having more than one processor results in increased efficiency.
- Each of the processors have their own local bus to access the local memory/I/O devices. This makes it easy to achieve parallel processing.
- The system structure is flexible, i.e. the failure of one module doesn’t affect the whole system failure; faulty module can be replaced later.


Great post. the information you shared is so informative and Its amazing. are you Looking for the best home elevators for your dream house.
ReplyDeleteArchitecture in Islamabad
Visit for movies IBOMMA
ReplyDeleteegg rate today
ReplyDelete